- Apply the scoring rubric to your problem
- If you did not receive your problem back send me an email
- see your class policy about sending emails
- Continue to work on Chapter problems in the interim
- Draw and Label Diagrams
- Identify POI
(PUK) - Any Problems post to the Blog/Discuss
Wednesday, November 26, 2014
HAPPY THANKSGIVING!!!!
Saturday, November 22, 2014
Problems Set On Calendar
You should be able to set up all the problems but are not expected to solve any past #24.
That means Picture/Unknowns/Knowns
The Equation for most of the problems will be F=ma
In addition to the problems complete the WS Free Body Diagrams Revisited
Sample Problem & Notes
That means Picture/Unknowns/Knowns
The Equation for most of the problems will be F=ma
In addition to the problems complete the WS Free Body Diagrams Revisited
Sample Problem & Notes
Sunday, November 16, 2014
Forces
F=MA
After studying the material of this chapter, you should be able to:
1. State Newton's three laws of motion and give examples that illustrate each law.
2. Explain what is meant by the term net force.
3. Use the methods of vector algebra to determine the net force acting on an object.
4. Define each of the following terms: mass, inertia, weight and distinguish between mass and weight.
5. Identify the SI units for force, mass, and acceleration.
6. Draw an accurate free body diagram locating each of the forces acting on an object or a system of objects.
7. Use free body diagrams and Newton's laws of motion to solve word problems.
After studying the material of this chapter, you should be able to:
1. State Newton's three laws of motion and give examples that illustrate each law.
2. Explain what is meant by the term net force.
3. Use the methods of vector algebra to determine the net force acting on an object.
4. Define each of the following terms: mass, inertia, weight and distinguish between mass and weight.
5. Identify the SI units for force, mass, and acceleration.
6. Draw an accurate free body diagram locating each of the forces acting on an object or a system of objects.
7. Use free body diagrams and Newton's laws of motion to solve word problems.
Thursday, November 13, 2014
Range equation
Develop a range equation in terms of the variables angle,height,initial launch velocity and gravity.
Case 1: object shot from the ground to the ground
Case 2: object shot from a cliff to the ground
Note: these are really the same equation, But the first is a simplified version and should be easier to figure out and understand.
SHOW ALL WORK.
If you complete this and get bored try to solve the equation for the angle. Do not start from scratch just use some algebra to rearrange the equation you already have.
Thursday, November 6, 2014
Want to Work for the FBI?
Have you ever seen the movie "Shooter"?
This problem can give you an idea to narrow the possibility and parameters of an investigative search.
Want 10 Free test Points?
Complete the problem below with all work shown on a SPOP w/ NDPS
SPOP- Separate Piece of Paper
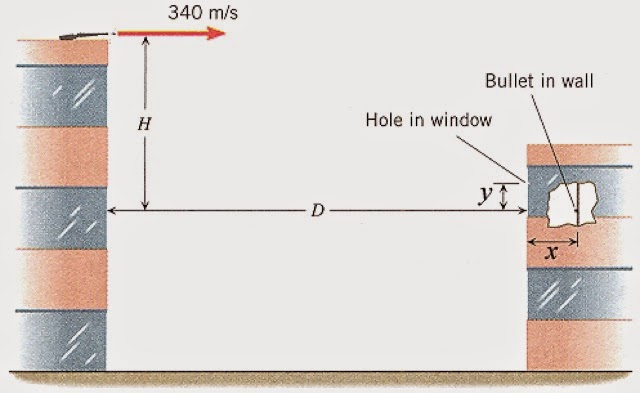
ssm 3.43 From the top of a tall building, a gun is fired. The bullet leaves the gun at a speed of 340 m/s, parallel to the drawing shows, the bullet puts a hole in a window of another building and hits the wall that faces the window. Using the data in the drawing, determine the distances D and H, which locate the point where the gun was fired. Assume that the bullet does not slow down as it passes through the window.
This problem can give you an idea to narrow the possibility and parameters of an investigative search.
Want 10 Free test Points?
Complete the problem below with all work shown on a SPOP w/ NDPS
SPOP- Separate Piece of Paper
- Remember identify the critical points in the diagram (Put labels of unknowns in the digram)
- In case you missed label the bajesus out of your diagram (See above)
- Write down key/critical quantities (Like the hunter in the monkey)
- Try to solve for those first
- Why this is more difficult... you may have to solve for several key piece of information first
ssm 3.43 From the top of a tall building, a gun is fired. The bullet leaves the gun at a speed of 340 m/s, parallel to the drawing shows, the bullet puts a hole in a window of another building and hits the wall that faces the window. Using the data in the drawing, determine the distances D and H, which locate the point where the gun was fired. Assume that the bullet does not slow down as it passes through the window.
Wednesday, November 5, 2014
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)